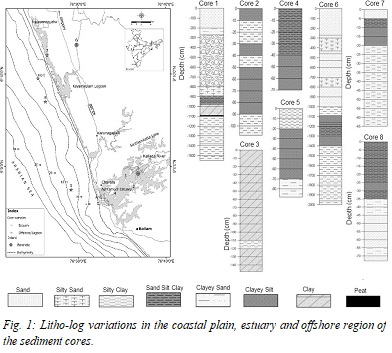
 Recurrent sea-level changes are reflected in the formation of coastal landforms; estuary, lakes, lagoons and barrier beaches during the late Quaternary period along the Kerala coast, SW India. The sediment core from these landforms was addressed for sediment lithofacies, geochemical parameters and associated foraminiferal assemblages to reconstruct the late Quaternary environment. The textural characteristics of the sediment indicate a shallow marine to lagoon and swampy/marsh environment. A layer of coarse sandy sediment (7–9 m thickness) is overlying the late Pleistocene (40 Kyrs BP) sediment sequence. The sediment was deposited under violent to the calm environment attributing its deposition in diverse energy regimes. This is also corroborated with the micro-textures of quartz grains. The geochemical elemental relationship (Rb vs K2O, Ni vs TiO2, K2O/Na2O vs SiO2/Al2O3, discriminant function) is established with paleoweathering, provenance and tectonic setting. An abundant population of Ammonia beccarii, A. tepida, E. discoidale, N. scaphum. A. beccarii in the sediments reveals their high tolerance and adaptability to the changing environment. The multiproxy studies on sediments, support a stronger monsoon in the early Holocene leading to the incursion of high-water levels, increased flow discharge and bottom scouring but, weak monsoon and arid climate prevailed during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). A conceptual model is proposed to depict the shoreline evolution and its climate.
Recurrent sea-level changes are reflected in the formation of coastal landforms; estuary, lakes, lagoons and barrier beaches during the late Quaternary period along the Kerala coast, SW India. The sediment core from these landforms was addressed for sediment lithofacies, geochemical parameters and associated foraminiferal assemblages to reconstruct the late Quaternary environment. The textural characteristics of the sediment indicate a shallow marine to lagoon and swampy/marsh environment. A layer of coarse sandy sediment (7–9 m thickness) is overlying the late Pleistocene (40 Kyrs BP) sediment sequence. The sediment was deposited under violent to the calm environment attributing its deposition in diverse energy regimes. This is also corroborated with the micro-textures of quartz grains. The geochemical elemental relationship (Rb vs K2O, Ni vs TiO2, K2O/Na2O vs SiO2/Al2O3, discriminant function) is established with paleoweathering, provenance and tectonic setting. An abundant population of Ammonia beccarii, A. tepida, E. discoidale, N. scaphum. A. beccarii in the sediments reveals their high tolerance and adaptability to the changing environment. The multiproxy studies on sediments, support a stronger monsoon in the early Holocene leading to the incursion of high-water levels, increased flow discharge and bottom scouring but, weak monsoon and arid climate prevailed during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). A conceptual model is proposed to depict the shoreline evolution and its climate.
Bibliographic Info: Varghese T. I., Prakash, T N., Sheela Nair, L., Sreenivasulu, G., Nagendra, R. [2021]. Reconstruction of the paleoenvironment of the late Quaternary sediments of the Kerala coast, SW India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, Vol. 222, Art. 104952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104952




 RTI Act
RTI Act
